A magnetically coupled pump, also called a magnetic drive pump, is a traditional pump assembly with a magnetic drive system.
Since the magnets in the inner and outer rings are attracted to each other, as the electric motor rotates the outer magnetic ring, the inner ring rotates at the same speed, which then rotates the impeller and causes the liquid to be pumped.
In a magnetically coupled pump, the liquid is completely contained without the use of any mechanical seals.
A coupling is a device or piece of machinery primarily used to connect two shaft ends together, especially for power transmission. It allows for some degree of end movement between the connecting ends while absorbing any misalignment (mounting error).
There are different types of coupling. Examples include flexible coupling, rigid coupling, split muff coupling, gear coupling, flange coupling, diaphragm coupling, jaw coupling and fluid coupling.
Couplings serve a few purposes:
Magnetic coupling is a kind of coupling that allows power transmission from one shaft to another by using magnetic fields rather than a mechanical part. This transmission happens through a non-magnetic containment barrier without physical contact between the shafts.
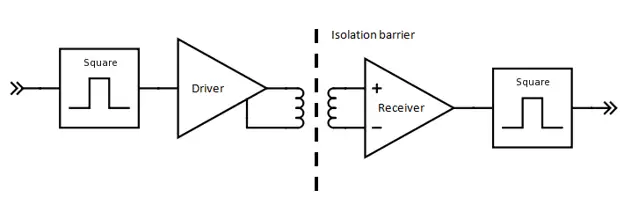
The two main types of magnetic coupling are:
Magnetic coupling removes any possibility of leakages or contamination from spillage since the containment barrier separates any contact of the liquid with the shaft or the couplings. This is why they are mostly used in pumps, propeller systems, and liquid environments.
Pumps with magnetic coupling are also called magnetic drive pumps or magnetic pumps. Magnetically coupled pumps are used in sewage, petroleum, water, and petrochemical fluid pumping.
They are also used to transfer dangerous liquids like sulphuric or hydrochloric acid, alkalis like caustic soda, corrosives and different kinds of pollutants like nitrogen monoxide.

Magnetically coupled pumps use the attraction and repulsion forces between opposite polarity magnets positioned on the coupling halves (opposite pairs of rotors/discs) to create a sort of magnetic flux.
In simple terms, it works on the fundamental principle that opposite magnetic poles attract. This attraction moves the shafts transmitting torque from the driving member of the coupling to the driven member.
Since there is no mechanical connection between the electric motor shaft and the impeller, seals are unnecessary. In mechanical pumps, seals are critical to preventing fluid leaks or contamination
Magnetically Coupled pumps have several specifications which influence their function. These include:
The principal advantage of magnetic coupling is that it removes the need for any rotating seals to transmit power (torque) between two rotating shafts. The containment “can” also acts as a barrier, thus practically reducing any leakage, contamination, or regular maintenance costs.
Other key advantages of magnetically coupled pumps include the following:
These advantages of magnetic coupling are also found in turbine pumps, side-channel pumps, and internal/external gear pumps.
The numerous advantages of magnetically coupled pumps make it an essential application in many industries. Some of the critical areas include:
Magnetically coupled pumps are used to pump and transmit highly abrasive liquid media. Examples of corrosive liquids are sulphuric acid, chromic acid gas, acetic acid and nitric acid. Alkaline solutions like Ammonium hydroxide, Calcium hydroxide and sodium bicarbonate are dangerous and need managing with care.
Medical Instruments
Used in the transmission of liquids and ultra-pure water in medical devices.
Robotics
Magnetically coupled dielectric elastomer pumps are used in soft robotics.
Food processing
Use of magnetically coupled pumps in the pumping of detergents used to clean pipes and processing equipment is important
Waste and Water Management
In the water treatment industry, magnetically coupled pumps are used to administer various cleaning chemicals in nanofiltration.
Chemical stocking
Transfer of dangerous liquids or chemicals from huge tanks to smaller containers
Surface Treatments
Used in the filtering and transfer of surface treatment chemicals and bath
Underwater application Industries
Magnetically coupled pumps are increasingly used in diver propulsion and remote-operated underwater vehicles.
The different advantages of magnetically coupled pumps make it an essential tool of the industrial age. With advances in pump technology, manufacturers are coming up with new designs that are smaller in size but boast double efficiency and power.
1. Engineering, C. (2016, August 29). Magnetically Coupled Pumps: Structure, Function and Best Practice. Chemical Engineering.
https://www.chemengonline.com/magnetically-coupled-pumps-structure-function-best-practice/
2. Hubing, T. (n.d.). LearnEMC – Introduction to Magnetic Field Coupling. Learn Emc.
Retrieved January 27, 2022,
https://learnemc.com/magnetic-field-coupling
3. Magnetically coupled pumps. (n.d.). HERMETIC Pumps – Sealless Pump Technology in Germany.
Retrieved January 27, 2022,
https://www.hermetic-pumpen.com/en/chemical/magnetically-coupled-pumps
4. StackPath. (n.d.). Processing Magazine.
Retrieved January 27, 2022,