Elution and adsorption are both surface phenomena and are applied as separation techniques to remove a substance from its source.
Elution is the process of removing or extracting one material from another by washing the analyte with a solvent whereas adsorption is the uptake of a substance by the surface of a solid material due to intermolecular attraction between them.
Adsorption is a rate-based separation technique that is largely dependent on factors like temperature, pressure, and pH. The main factor of the adsorption process, however, is the nature of the adsorbent being used. The fundamentals of adsorption lies on the surface affinity between the adsorbate and adsorbent.
Adsorbents are characterized by high porosity and have rough surfaces implying a larger surface area for adsorption. Silica gel, zeolites, and activated carbons are the common adsorbents used due to their high surface area.
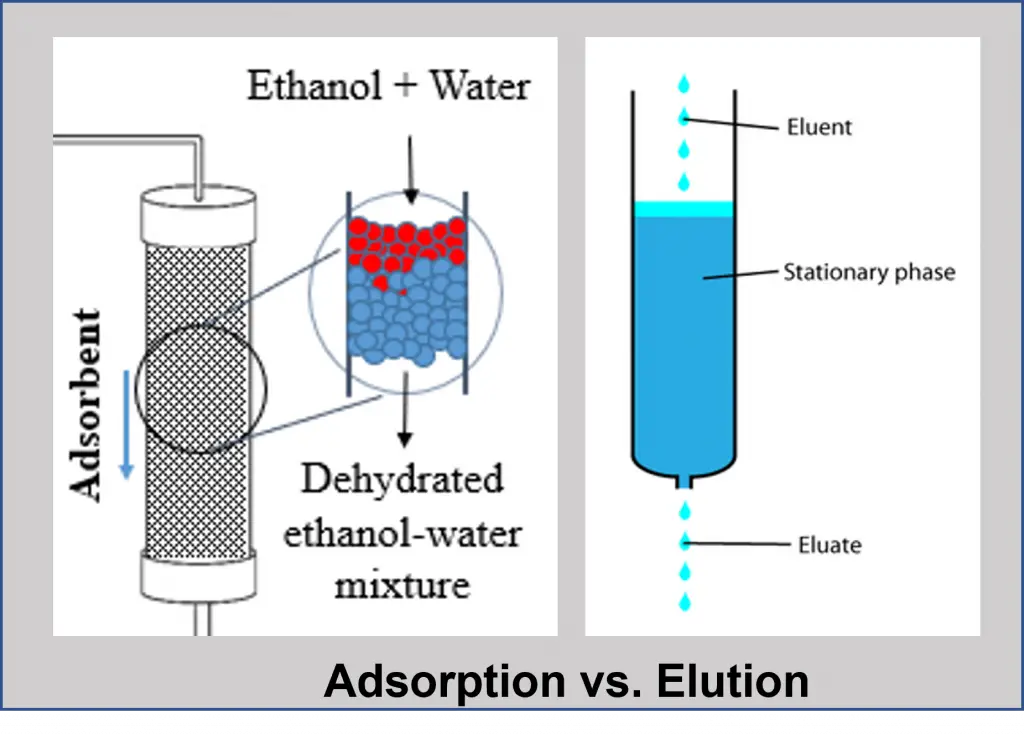
Both sorption processes, elution and adsorption are closely associated together in adsorption column chromatography. It is a chromatographic process using a solid/adsorbent as a stationary phase and a mobile phase that is either a gas or liquid. Here’s how the elution technique works:
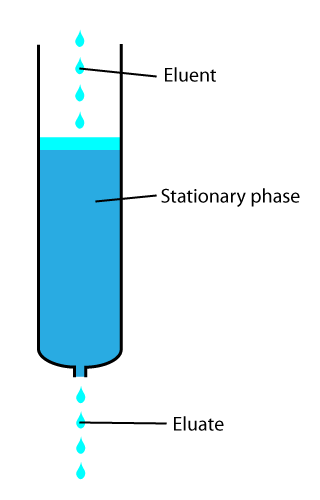
During adsorption, the adsorbent adsorbs a specific analyte as it passes through the column. The elution technique is used to remove the analyte by running the column with a solvent (called “eluent”). The solvent either passes by the adsorbent/analyte complex or displaces the analyte by binding to the adsorbent. The solvent which isolates the analyte (called the “eluate”) from the bulk material goes out the column.
One particular application of the elution process is in medicine. Elution is commonly used to concentrate and solubilize antibodies from red blood cells (RBCs) for subsequent identification studies.
In this case, the eluent is acidic glycine which removes the antibodies from the red blood cells. While the eluate is the supernatant fluid (antibodies-containing solvent) which is further filtered out through centrifugation. Finally, the antibodies are then tested
Although elution is often associated with adsorption, the two must be well distinguished from one another by how they separate mixtures. In summary:
In medicine, an elution test is performed to separate antibodies from the cells in order to examine these antibodies for possible disease identification studies.
Siracusa used the adsorption-elution technique for the first time for medical applications. He is a forensic scientist that used the absorption-elution technique in 1923 for the ABO blood group typing of bloodstains.
Adsorption is used in blood banking to bind antibodies to red blood cells in order to remove them from the plasma and analyze them.